Economic developments in the European Union

The German economy is expected to contract by 0.2% this year, the economy ministry said. The government is thus lowering its forecast for a 0.3% contraction this year. It will be the second year in a row for Europe’s largest economy, which was the weakest among its large eurozone peers last year, to see a 0.3% drop in gross domestic product. Germany’s leading economic institutes also cut their forecasts for 2024 at the end of September and expect the economy to contract by 0.1% in their autumn economic forecasts. European Central Bank Governing Council member Pierre Wunsch warned against cutting interest rates too quickly and said he was undecided about a widely expected rate cut this month, according to Belgian newspaper L’Echo. French central bank governor François Villeroy de Galhau said: “A cut is very likely and it won’t be the last, the rhythm depends on how the fight against inflation develops.” More than 90% of economists polled by Reuters expect a cut in interest rates next week. A similar number of economists also expect another interest rate cut in December.
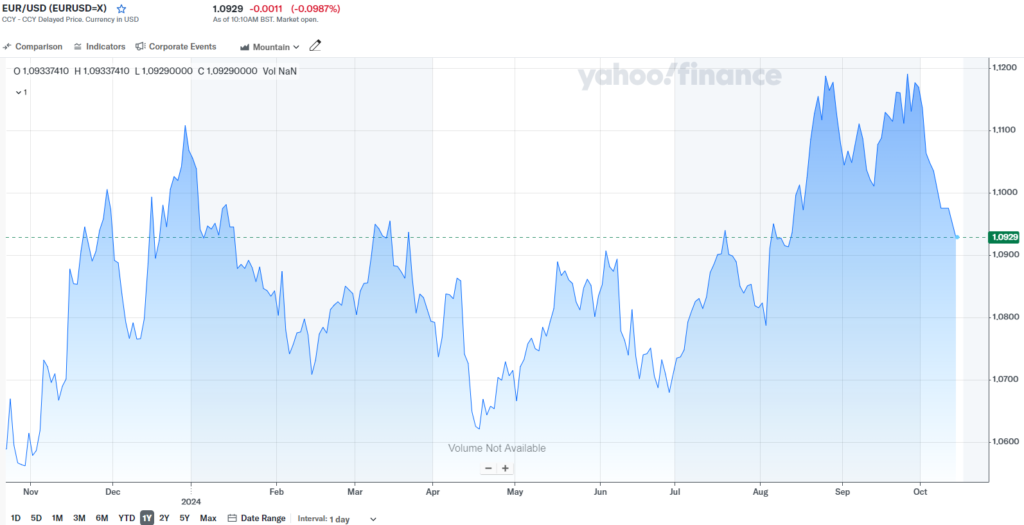
The European Central Bank has already cut interest rates twice this year, and the next cut is expected on 17 October 2024, to 3.5%. This cut is also anticipated by financial markets, where investors are expecting the ECB to pick up the pace of monetary easing given the weak economy. Financial analysts expect the ECB deposit rate to fall to 3% by the end of 2024 and 2% by the end of 2025, with much of the financial community already considering this 2% interest rate to be neutral and not stimulating or slowing economic growth. The Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Kristalina Georgieva, says that Europe must start preparing for further shocks in order not to be left behind. The IMF also recommends that Europe stick together in the face of the fragmentation of the EU single market and avoid a financial crisis while the world grapples with crises such as COVID, the war in Ukraine and the Middle East.
Inflation in the EU %
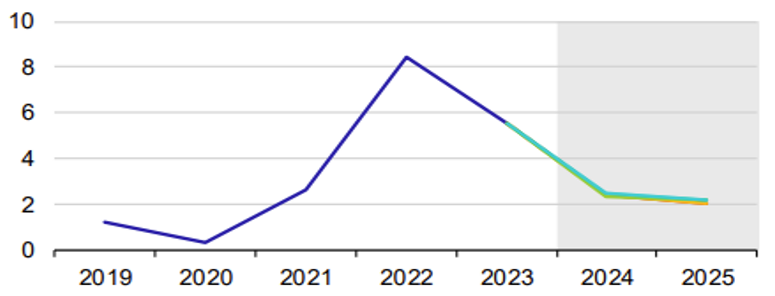
World economists expect an investment-led recovery in the coming year. Monetary policy is expected to start on the side of base rates. In the euro area, we expect the inflation target to be reached in the first half of 2026. Uncertainties and risks that may adversely affect the economic outlook of the EU, but also the world, have increased in recent months due to Russia’s protracted war against Ukraine and geopolitical tensions. If there are any negative significant developments in the world, some EU Member States could take additional measures for 2025, i.e. fiscal consolidation, which could impact economic growth next year. Climate change is also weighing on the current outlook of global economists.